The USA and Mexico geographical, cultural, and political landscapes make these two neighboring countries pivotal players in North America. Their border region spans deserts, rivers, and bustling cities, reflecting shared and distinct identities. This article provides a detailed look at the Map of USA and Mexico, focusing on boundaries, key geographical features, political divisions, and how the maps shape our understanding of this region in 2024.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of the USA-Mexico Border
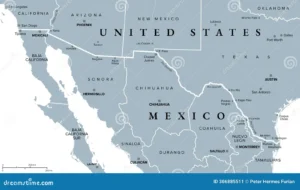
The USA-Mexico border stretches over 3,145 kilometers (1,954 miles)from the Pacific Ocean west to the Gulf of Mexico east. This international boundary runs through four U.S. states(California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas) and six Mexican states(Baja California, Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas). This frontier is not just a dividing line but a dynamic zone of commerce, migration, and cooperation between the two countries.
Key Crossing Points
Prominent border crossings include Tijuana-San Diego, Ciudad Juárez-El Paso, and Laredo-Nuevo Laredo. The Rio Grande River defines much of the border, particularly along Texas, where multiple ports of entry facilitate trade and human movement.
The USA Map: Geography and States

The USA spans 9.8 million square kilometers, making it the third-largest country globally by land area. It consists of 50 states, each with unique characteristics. The nation features diverse landscapes, including mountains (the Rockies), vast plains, and coastlines along the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Major cities such as New York, Los Angeles, and Chicago are finance, culture, and innovation hubs.
Notable Features:
- National Parks: The USA is home to iconic national parks like Yellowstone and the Grand Canyon.
- Water Bodies: The Great Lakes in the northeast and the Gulf of Mexico along the southern coast shape much of its geography.
The USA shares its southern border with Mexico, making cross-border cooperation essential for migration control, environmental preservation, and trade.
The Mexico Map: Geography and States
Mexico covers an area of 1.97 million square kilometers, making it the 13th largest country in the world. Politically, it is divided into 32 federal entities, including 31 states and the capital, Mexico City. It is a country rich in biodiversity, with coastal areas along the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico.
Important Regions:
- The Yucatán Peninsula: Known for its tropical climate and archaeological sites.
- Baja California Peninsula: A desert region extending southward from the U.S. border.
- Rio Grande (Río Bravo): Forms a significant part of the border with Texas.
Mexico’s cities, such as Mexico City, Guadalajara, and Monterrey, are vital cultural and economic hubs in Latin America. Mexico’s geography, marked by highlands and coastal plains, offers diverse ecosystems.
Trade and Infrastructure Along the Border
The USA and Mexico maintain one of the world’s most robust trade partnerships. As of 2024, over $600 billion in goods flow between the two nations annually. Border cities like Tijuana and San Diego are crucial in facilitating commerce. The region also contains a well-developed transport network, including railroads, highways, and airports, enabling the smooth flow of goods and people.
Environmental and Social Challenges
Both countries face shared challenges related to environmental degradation and cross-border migration. The Sonoran Desert and other arid regions are particularly vulnerable to climate change, impacting water resources. The border also sees significant migratory movements, necessitating cooperation on immigration policies and border security.
USA-Mexico Border Security and Migration Trends
The USA-Mexico border is a focal point for immigration, security, and economic policies in both nations. The complex migration patterns involve people from Mexico and Central America seeking asylum or better economic opportunities in the United States. Border security measures have evolved, with increased fencing, surveillance, and policies to manage immigration flows.
Recent Developments in 2024
- Border Wall and Technology Enhancements: While physical barriers such as the border wall remain, drones, sensors, and surveillance cameras play an increasingly important role in border monitoring.
- Migration Shifts: Notably, Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador have emerged as major sources of migrants, shifting the narrative beyond Mexican immigration alone.
Economic Impact: Immigration also has positive economic implications, contributing to the labor force, particularly in agriculture and construction industries across border states like Texas and California.
Tourism and Cultural Connections
The proximity of the USA and Mexico encourages vibrant tourism on both sides of the border. Mexico’s beach resorts in Cancun, Cabo San Lucas, and Puerto Vallarta attract millions of American tourists annually. Simultaneously, cities such as Los Angeles, New York, and Miami are popular destinations for Mexican visitors.
Cultural Exchange:
- Hispanic Heritage: Mexican culture has profoundly influenced the United States, especially in border states like California and Texas, with traditions, festivals, and cuisine becoming part of mainstream American life.
- Binational Events: Events like the San Diego-Tijuana Art Festival exemplify the cultural synergy across the border.
Geography and Environmental Considerations
The geography along the USA-Mexico border varies dramatically, from the Sonoran Desert to the lush valleys of the Rio Grande. Both countries face environmental challenges, including water scarcity, wildfires, and desertification, which necessitate collaborative solutions.
Environmental Initiatives:
- Rio Grande Management: Shared river systems require joint management to prevent overuse and pollution.
- Border Environmental Cooperation Commission (BECC): Aims to promote environmental sustainability in border regions.
Preserving natural landscapes such as Big Bend National Park in Texas and the Sierra Madre Occidental in Mexico is crucial for biodiversity conservation.
Political and Social Implications
The border is not just a geographic boundary but also a political flashpoint. Issues such as drug trafficking, human rights concerns, and national security regularly make headlines. The policies of both nations impact millions of residents in border communities, emphasizing the need for balanced immigration and economic policies.
Exploring Interactive Maps and Resources
Interactive maps are valuable tools for anyone studying or planning to travel across these two countries. Websites like Ontheworldmap offer detailed maps showing political boundaries, state capitals, and border crossings. Similarly, resources on World Atlas provide insights into topographical and political maps, enriching users’ understanding of the USA and Mexico’s landscapes
Maps and Travel Planning
For travelers and students alike, understanding the maps of the USA and Mexico is essential for navigating these vast nations. Resources like the interactive maps on Ontheworldmap allow users to explore detailed political boundaries, cities, and transportation routes. Printable versions are available for use in classrooms or for personal study.
Useful Travel Tips:
- Tourism: Mexico offers beautiful beach resorts, while the USA provides natural parks and vibrant cities.
- Border Crossings: It is essential to have proper documentation when crossing the USA-Mexico border.
Conclusion
The geographical relationship between the USA and Mexico is complex, defined by collaboration and challenges. Understanding their maps provides a clearer view of North America’s political, economic, and cultural dynamics. Whether for trade, tourism, or policy-making, these maps remain critical tools for fostering cooperation and growth.
In 2024, the interplay between these countries continues to evolve, underscoring the importance of geography in international relations. Users can stay informed about this dynamic region with updated maps and resources readily available online.
FAQ
How long is the USA-Mexico border?
The USA-Mexico border stretches approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers). It starts at the Pacific Ocean in the west, follows the Rio Grande River for much of its length, and ends at the Gulf of Mexico. It includes both land and maritime boundaries, crossing a variety of terrains from deserts to urban areas.
What are the main border crossing points between the USA and Mexico?
There are 47 active land ports of entry along the border, facilitating legal crossings and trade. Key crossings include Tijuana-San Diego, El Paso-Ciudad Juárez, and Laredo-Nuevo Laredo. These hubs handle most cross-border trade and daily human movement between the two nations.
How do the maps of the USA and Mexico represent political boundaries?
The Map of USA and Mexico both two countries showcase 50 states in the USA and 32 federal entities in Mexico, including Mexico City. These maps highlight state capitals, major cities, roads, and natural boundaries such as rivers. Political maps emphasize clear demarcations for governance and jurisdiction purposes.
What environmental challenges affect the border region?
Both countries face environmental challenges along the border, such as water scarcity and desertification. Rivers like the Rio Grande are essential resources for communities on both sides but are under strain due to climate change and overuse. Conservation efforts are vital to maintaining the ecological health of this area.
How are maps useful for travel planning between the USA and Mexico?
Travelers often use Map of USA and Mexico maps to explore routes, cities, and transportation networks across the two countries. Rand McNally atlases and online tools like Ontheworldmap provide practical information for road trips, trade routes, and tourism, including details about toll roads and national parks.
What role does the USA-Mexico border play in trade?
The border is a critical trade gateway, with the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) boosting cross-border commerce. Mexico is a major export partner for the USA, and trade hubs like Laredo facilitate the seamless movement of goods, contributing to the economic growth of both nations.