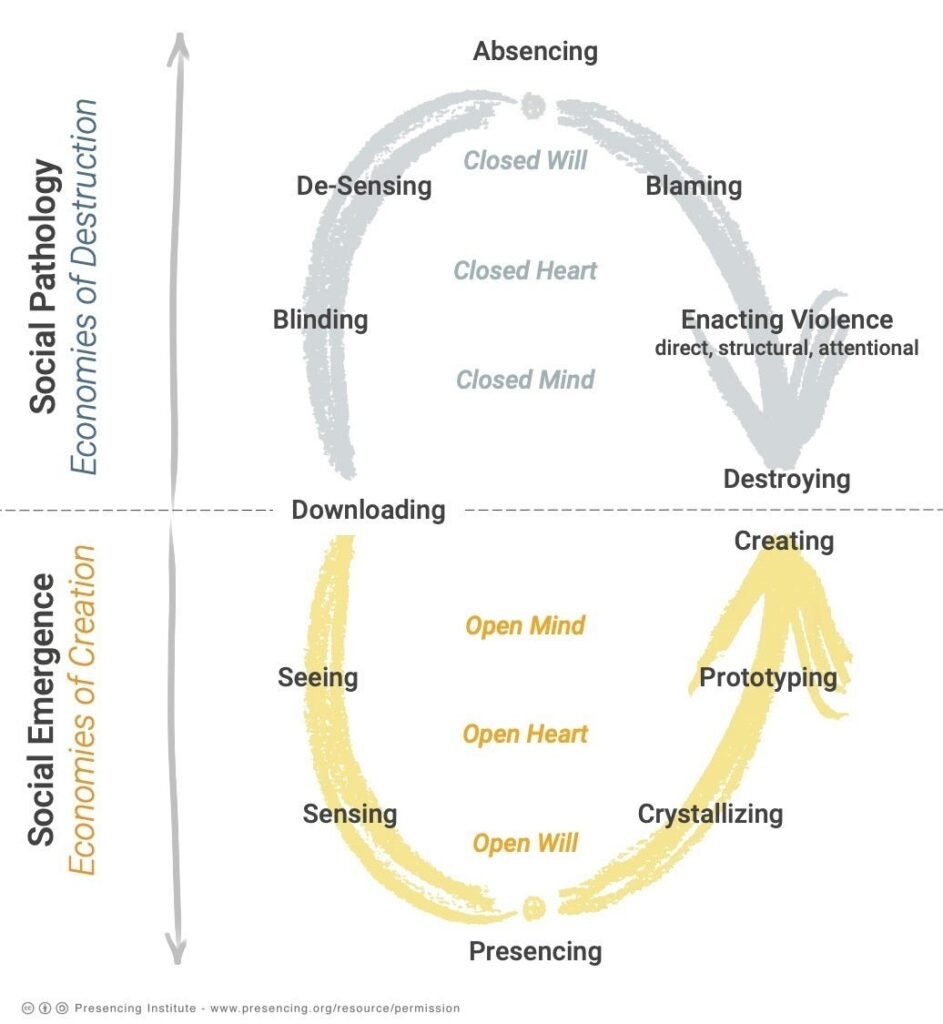
Absencing refers to the state of being absent or the act of not being present at a usual or expected place. It is characterized by a closed mind, closed heart, and closed will, leading to self-destruction and a lack of collective creativity.
On the other hand, presencing involves operating from an open mind, open heart, and open will, leading to collective creativity and a social field of positive transformation. The concept of absencing and presencing is often associated with Theory U, a framework for societal and systems transformation.
By understanding and actively choosing to operate from a state of presencing, individuals and organizations can foster creativity and positive change.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Essence Of Absencing
Absencing is the state of being absent, a failure to be present. It is a choice to operate from a closed mind, heart, and will, leading to self-destruction. In contrast, presencing is the choice to operate from an open mind, heart, and will, fostering collective creativity.
Defining Absencing
Absencing refers to a state of being absent or disconnected from oneself, others, and the world around us. It is a form of self-destruction that arises from operating with a closed mind, heart, and will. Absencing is characterized by denial, blame, and destruction, and it can lead to negative social fields and collective outcomes.Absencing Vs. Presencing
On the other hand, presencing is the ability to be present, open, and receptive to oneself and others. It involves operating with an open mind, heart, and will and being connected to one’s emerging future self. Presencing leads to positive social fields and collective outcomes, such as creativity, innovation, and transformation. The key difference between absencing and presencing is the orientation towards self and others. Absencing is a self-centered approach, while presencing is a more other-centered approach. In other words, absencing is focused on the past, while presencing is focused on the future. To sum up, the essence of absencing lies in the failure to be present and connected to oneself, others, and the world around us. It is a form of self-destruction that arises from operating with a closed mind, heart, and will. In contrast, presencing is the ability to be present, open, and receptive to oneself and others, and it leads to positive social fields and collective outcomes.Roots Of Absencing
Absencing is a concept that delves deep into the human psyche and societal dynamics, exploring the reasons behind the failure to be present or the state of being absent. Understanding the roots of absencing requires us to examine its historical context and psychological underpinnings.
Historical Context
In order to grasp the roots of absencing, it is essential to consider its historical context. Throughout history, societies have been shaped by various factors such as power dynamics, cultural norms, and societal structures. These factors have influenced individuals and groups in different ways, often leading to the phenomenon of absencing.
The historical context of absencing can be traced back to instances where certain individuals or communities have been marginalized, oppressed, or excluded. This exclusion can be based on factors such as race, gender, class, or any other form of discrimination. The resulting absence of these individuals or communities from the societal narrative can have a profound impact on the collective consciousness.
Psychological Underpinnings
Examining the psychological underpinnings of absencing provides further insight into its roots. Absencing can be seen as a defense mechanism or coping strategy that individuals employ in response to challenging or threatening situations. It is a way to detach oneself from the present reality and avoid confronting uncomfortable truths.
One psychological aspect that contributes to absencing is the fear of change. Humans tend to resist change, as it often brings uncertainty and challenges existing beliefs and norms. This fear of the unknown can lead individuals to withdraw, disengage, or ignore the issues at hand, resulting in absencing.
Another psychological factor is the tendency to prioritize self-interest over collective well-being. When individuals become solely focused on their own needs and desires, they may neglect or overlook the needs and experiences of others. This self-centeredness can perpetuate absencing, as it hinders empathy and understanding.
Moreover, absencing can also be fueled by cognitive biases and blind spots. Our brains have a natural inclination to filter information and perceive the world through our own preconceived notions and biases. These cognitive processes can limit our ability to fully acknowledge and engage with different perspectives, leading to absencing.
In conclusion, understanding the roots of absencing requires an exploration of its historical context and psychological underpinnings. By recognizing the societal and individual factors that contribute to absencing, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and aware society.
Recognizing Absencing Patterns
Absencing, a concept coined by MIT lecturer Otto Scharmer, refers to a state of being absent or disconnected from oneself and others. It involves a lack of presence and awareness, which can manifest in various behavioral and cognitive patterns. Recognizing these patterns is crucial for individuals and organizations to address and transform them effectively.
Common Behavioral Indicators
When individuals are experiencing absencing, they may exhibit certain behavioral indicators that signal their disconnection from the present moment and their true selves. These indicators include:
- Withdrawal from social interactions
- Lack of active participation in discussions or activities
- Frequent distractions and inability to focus
- Emotional detachment and apathy
- Resistance to change or new ideas
Cognitive Signs Of Absencing
In addition to behavioral indicators, there are cognitive signs that reflect the presence of absencing. These signs are related to an individual’s thought patterns and mental processes, including:
- Repetitive negative self-talk and limiting beliefs
- Rigid adherence to familiar routines and perspectives
- Inability to envision or pursue future possibilities
- Lack of empathy and understanding towards others
- Difficulty in accessing creativity and innovative thinking

Credit: managementinnovations.wordpress.com
Impact Of Absencing On Creativity
Absencing, the state of being absent, can have a significant impact on creativity. When we operate from a closed mind, heart, and will, we give rise to a social field of self-destruction. In contrast, operating from an open mind, heart, and will can foster collective creativity and presencing.
Absencing, the state of being absent or disconnected from one’s true self and the emerging future, can have a profound impact on creativity. When individuals or organizations experience absencing, they may face barriers to innovation, hindering their ability to generate novel ideas and solutions. Additionally, absencing can lead to a lack of empathy, disconnection from one’s potential, and a rigid adherence to existing identities, all of which stifle creativity.
Barriers To Innovation
When absencing occurs, individuals and teams may encounter several barriers to innovation, including:
- Lack of empathy and understanding of others’ perspectives
- Resistance to change and a rigid adherence to existing identities
- Inability to envision and embrace emerging future possibilities
- Disconnected from one’s true self, limiting creative expression
Case Studies: Absencing In Action
Several real-world examples demonstrate the impact of absencing on creativity. In these case studies, we observe how absencing has led to the stifling of innovative thinking and the hindrance of creative potential. By understanding these instances, we can gain insights into the detrimental effects of absencing and the importance of fostering a culture of presence and connection to enable creativity to flourish.
Absencing In Social Systems
Absencing is a term coined by Otto Scharmer, which refers to the state of being absent or disconnected from oneself, others, and the environment. This phenomenon is prevalent in social systems, including teams and organizations, and can have significant effects on their dynamics and success.
Effects On Team Dynamics
Absencing can create a negative impact on team dynamics, leading to poor communication, lack of trust, and low morale. When team members are not present or connected to each other, they tend to focus on their individual goals and priorities, neglecting the team’s objectives. This can result in conflicts, misunderstandings, and reduced productivity.
Moreover, absencing can hinder creativity and innovation, which are essential for team success. When team members are disconnected from their inner selves and the emerging future, they are less likely to come up with new ideas and solutions to complex problems. As a result, teams that operate from a state of absencing are less competitive and adaptable in today’s rapidly changing environment.
Organizational Challenges
Absencing can also pose significant challenges to organizations, affecting their culture, strategy, and performance. When leaders and employees are not present or connected to the organization’s purpose and values, they tend to focus on short-term goals and profits, neglecting the long-term sustainability and social impact.
Furthermore, absencing can create silos and divisions within the organization, as employees and departments operate in isolation and competition rather than collaboration and synergy. This can result in redundancy, inefficiency, and missed opportunities for growth and innovation.
Finally, absencing can hinder organizational learning and development, as employees are less likely to reflect on their actions and feedback, and less open to new perspectives and feedback. This can result in stagnation and decline, as organizations fail to adapt to changing market and customer needs.
In conclusion, absencing is a significant challenge for social systems, including teams and organizations. To overcome this challenge, it is essential to cultivate a culture of presencing, where team members and leaders are present, connected, and open to learning and innovation. This requires a shift in mindset and behavior, from ego-system thinking to eco-system thinking, where the well-being of the whole is as important as the individual.
Techniques To Counteract Absencing
Counteracting absencing requires a shift from a closed mindset to an open one, embracing creativity and collective growth. By moving away from denial, blame, and destruction, individuals can foster a social field of self-awareness and empathy. This transformative process, known as presencing, enables us to create a positive impact on ourselves and the world around us.
Techniques to Counteract Absencing Absencing is a common phenomenon that occurs when we disconnect from our inner self, others, and the present moment. It can lead to feelings of disconnection, apathy, and lack of purpose. However, there are ways to counteract absencing and cultivate a deeper sense of presence and connection. Here are some techniques to try:Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness practices involve paying attention to the present moment and accepting it without judgment. This can help us become more aware of our thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations. Some mindfulness practices to try include:- Body scan meditation
- Breathing exercises
- Walking meditation
- Yoga
Embodied Exercises
Embodied exercises involve using the body to cultivate a deeper sense of presence and connection. These exercises can help us become more aware of our body and its sensations. Some embodied exercises to try include:- Grounding exercises
- Dance/movement therapy
- Body-based psychotherapy
- Qi Gong
Developing A Practice Of Presence
Absencing, the state of being absent or the failure to be present at a usual or expected place, is a concept that has significant implications in our personal and professional lives. Developing a practice of presence is essential to counter absencing and cultivate a mindset of openness and connectivity. By nurturing daily habits for presence and fostering a sense of connection with our inner selves and the world around us, we can actively combat the detrimental effects of absencing.
Daily Habits For Presence
To develop a practice of presence, incorporating daily habits that promote mindfulness and self-awareness is crucial. This can include:
- Engaging in regular meditation or breathing exercises to center the mind and body
- Setting aside dedicated time for reflection and introspection
- Practicing gratitude and acknowledging the present moment
Cultivating Openness And Connectivity
Another integral aspect of developing a practice of presence involves cultivating openness and connectivity. This can be achieved through:
- Active listening and empathetic communication with others
- Engaging in activities that foster a sense of community and belonging
- Embracing vulnerability and being open to new experiences
By integrating these daily habits and nurturing a mindset of openness and connectivity, individuals can effectively counter absencing and cultivate a deeper sense of presence in their personal and professional lives.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Transforming Absencing Into Presencing
Absencing, the state of being absent or disconnected, can hinder personal and collective growth. However, by transforming absencing into presencing, individuals and groups can unlock their potential for creativity and progress. This transformation involves leveraging personal insights and implementing strategies for collective creativity.
Leveraging Personal Insights
Individuals can leverage personal insights to transition from absencing to presencing. This involves cultivating self-awareness and mindfulness to recognize and address moments of disconnection. By acknowledging and understanding the underlying causes of absencing, individuals can take proactive steps to reconnect with themselves and others, fostering a more present and engaged state of being.
Strategies For Collective Creativity
Implementing strategies for collective creativity is essential for transforming absencing into presencing within groups and organizations. This may involve creating a supportive and inclusive environment that encourages open communication, empathy, and collaboration. By fostering a culture of active listening and shared vision, collective creativity can thrive, allowing for the co-creation of innovative solutions and meaningful outcomes.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between Absencing And Presencing?
Absencing is operating from a closed mind, heart, and will, leading to self-destruction. Presencing is choosing to operate from an open mind, heart, and will, fostering collective creativity.
What Is The Meaning Of Absencing?
Absencing refers to the state of being absent or the act of not being present at a usual or expected place. It can also describe a failure to see, feel, or act by closing oneself off from the world. In contrast, presencing involves being present, open-minded, and open-hearted, leading to collective creativity and transformation.
What Is The Concept Of Absencing?
Absencing refers to the state of being absent or failing to be present at a usual or expected place. It involves a disconnection from one’s emerging future self and getting stuck in rigid identities, leading to a lack of empathy and a closed-off mindset.
How Does Absencing Differ From Presencing?
Absencing and presencing are two contrasting ways of operating in the world. Absencing is characterized by closed-mindedness, a closed heart, and a closed will, resulting in self-destruction and separation. On the other hand, presencing involves an open mind, an open heart, and an open will, leading to collective creativity and connection with one’s emerging future self.
Conclusion
The concept of absencing highlights the choice between self-destruction and collective creativity. It reflects our ability to operate from a closed or open mindset, heart, and will, ultimately shaping the social field. Understanding absencing can empower individuals and organizations to actively choose a path towards collective creativity and positive transformation.